Introduction
Apache Kafka is a powerhouse in real-time data streaming, offering a straightforward way to connect data producers and consumers. This blog breaks down Kafka's core concepts, components, and real-world applications, all without the jargon.
Foundational Concepts
Topics and Partitions: Kafka organizes data into topics, like folders, each divided into partitions for efficient data distribution.
Producers and Consumers: Producers send data to topics, and consumers subscribe to topics for real-time data access.
Brokers and Clusters: Brokers store and distribute data; multiple brokers form a Kafka cluster for scalability.
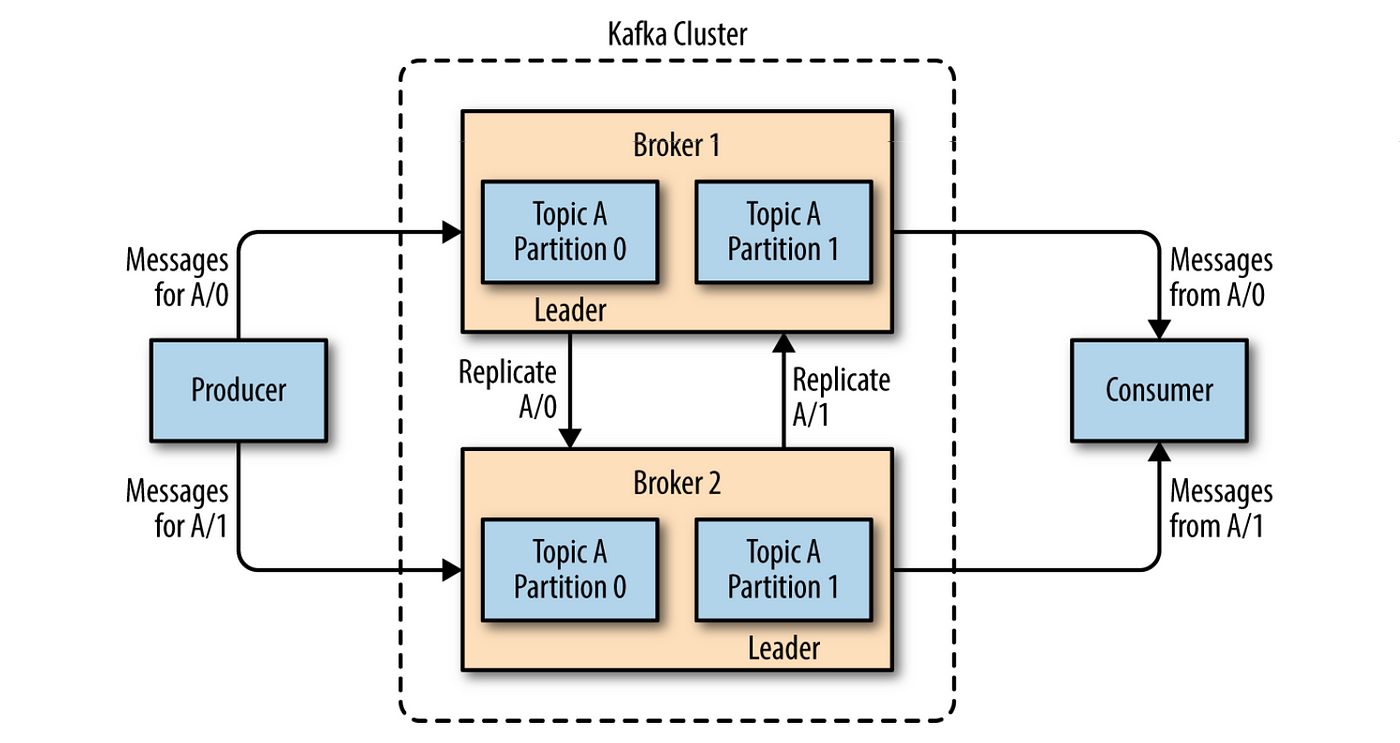
In-Depth Component Analysis
ZooKeeper: Manages Kafka clusters, configuration, broker health, and partition leadership.
Producers: Generate data, kickstarting data flow within Kafka.
Consumers: Receive and process data for real-time insights.
Connectors: Streamline data integration with external systems.
Streams: Process and analyze data within Kafka in real time.
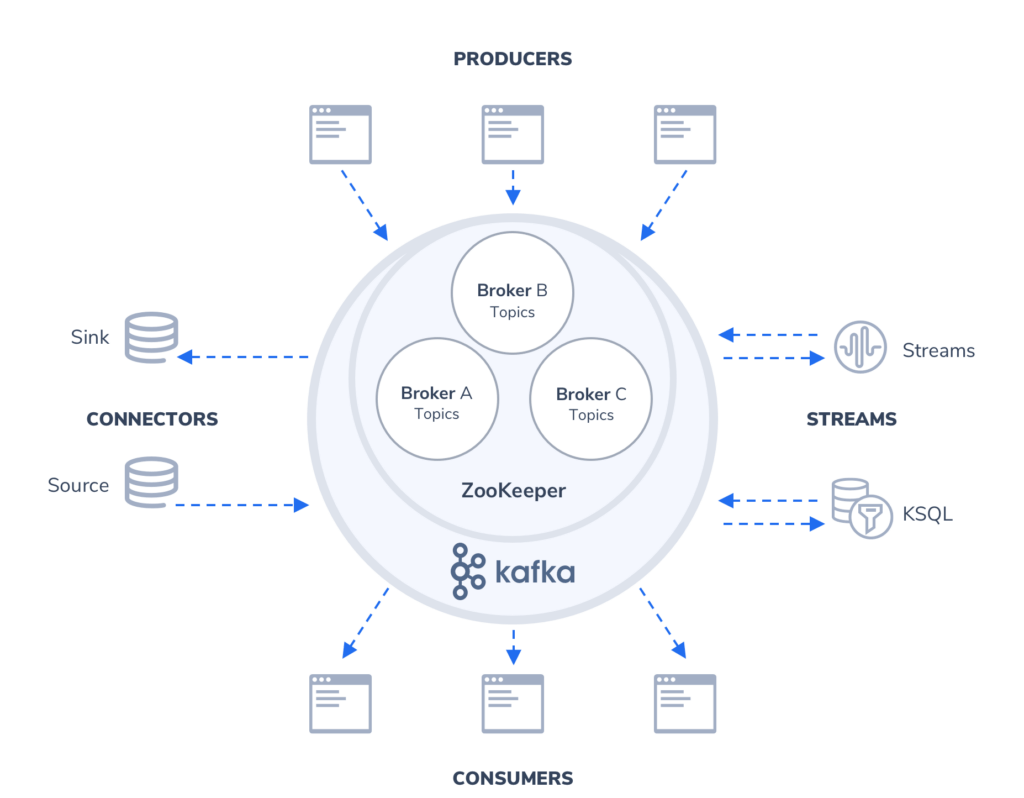
Data Path Tracing
Producers send data to specific topics, divided into partitions across brokers.
Consumers subscribe to topics, process data, and unlock real-time insights and actions.
Building a Resilient Architecture
Distributed Architecture: Kafka's distribution ensures high availability, fault tolerance, and scalability.
Replication and Fault Tolerance: Data replication ensures data availability even during failures.
Data Retention and Compaction: Control data retention and optimize storage with compaction.
Scaling for Performance
- Kafka scales horizontally, partitioning data for high throughput.
Guarantees and Durability
- Kafka maintains message ordering within partitions and ensures data integrity with replication.
Feature Integration
Distributed: Kafka handles large data volumes as a distributed system.
Event Streaming: Kafka streams data in real-time for instant processing.
Scalable: Kafka scales horizontally to meet growing data demands.
Fault Tolerant: Kafka continues functioning even with cluster node failures.
1M Requests per Second: Kafka handles high volumes of requests for responsive data processing.
Real-World Applications
Log Aggregation: Kafka centralizes logs for streamlined analysis.
Event Sourcing: Kafka captures immutable events for reliable auditing.
Data Integration: Kafka Connectors simplify data movement.
Monitoring and Metrics: Kafka's real-time capabilities excel in system health monitoring.
The Expansive Kafka Ecosystem
Kafka Streams: Empowers real-time data processing within Kafka.
Kafka Connect: Streamlines data integration with pre-built connectors.
Confluent Platform and Extensions: Expands Kafka's capabilities for comprehensive data streaming.
Architecting Triumph: Best Practices
Designing Topics and Partitions: Plan for performance and scalability.
Managing Data Retention: Optimize data storage with proper retention policies.
Strategizing Consumer Groups: Balance loads for efficient data processing.
Confronting Challenges
Consumer Offset Management: Critical for data integrity and loss prevention.
Schema Evolution: Kafka accommodates smooth data structure updates.
Monitoring and Troubleshooting: Key for maintaining a healthy Kafka deployment.
Conclusion
Apache Kafka's architecture empowers real-time data streaming without the complexity. By understanding its core components and best practices, organizations can harness Kafka for resilient, scalable, and high-performance data pipelines. This exploration provides a clear glimpse into Kafka's capabilities, promising insights for the data-driven future. Stay tuned for deeper dives into Kafka's architecture.
![]()
